Guardlets Simulator Description
Contents
- Overview
- Rules of Behavior
- Rules of
Evolution
- Changing the Population
Characteristics
- Discussion
Overview
Guardlets belong to the cooperative
agent family sharing the tendency to cooperate, and the lifelike emergent behavior
which is based on a few simple, local rules. . Guardlets are modeled using a Java
applet. The applet allows the changing of traits and personality of the population,
and also breeding and evolving the population.
The description below covers the
Guardlets applet.
Rules of Behavior
Guardlets behavior is governed by
two rules:
- A rule specifying how to relate
to one's own kind.
- A rule specifying how to relate
to Attackers.
Both Guardlets and Attackers are attracted
to the resource-critical center screen section. Guardlets attempt to limit excessive
access to this area.
1. How to relate to one's own kind
- Identify Guardlets that are near
to you and try to stay close to them, but not too close
2. How to relate to Attackers
- Interpose yourself between Attackers
and center section if an Attacker is too close for too long
Rules of Evolution
Guardlets evolve sexually,
where each Guardlet is the descendent of two parents. Mother and father are selected
according to the mechanism of 'Survival of the Fittest by Unnatural Selection'.
Asexual reproduction can occur with the last of the species. Fitness is defined
by three attributes; energy, safety, and cooperation. If you are a Guardlet, you
can gain or lose these during your lifetime, and the more you have, the fitter
you are.
These are the Rewards and Penalties
that influence fitness:
(The overall fitness is calculated as
a weighted function of energy, safety, and cooperation)
- Energy: Guardlets gain energy
when moving an Attacker away from the critical center section in proportion to
the distance from the center section. An analogy is crowd control where the
degree of control required is proportional to the proximity to a critical
area.
- Safety: Guardlets gain safety
by touching each other, keeping coherent ranks to provide defense.
- Cooperation: Guardlets gain cooperation
by moving toward each other.
Changing the Population Characteristics
How to use the applet
Modifying the static population
You can do the following:
- Go to 'Edit Properties' and modify
the environment, Click 'Update' to apply the new environment"
- Follow individual Guardlets easily
by displaying their ID numbers.
The' Show Numbers/Show Shapes' button toggles between these display modes.
- Turn off (or on again) the sound
effects.
- Display information on all Guardlets
by clicking the 'Show Info' button.
- Display a Help screen by the 'Show
Help' button.
- Select a predefined population
from the 'Predefined' screen.
- Reset everything to default by
clicking the Restart button.
Modifying the evolutionary factors
Evolution occurs when new generations
are formed from older ones. You can either create generations manually (click
the Breed button) or start a continuous process where new generations are created
based on timed cycles (click the Start Evolution button)
You can do the following:
- Modify the fitness function. Go
to 'Edit Properties' and assign Energy and Safety and Cooperation Weight Factors
- If Energy weight is higher,
Guardlets will evolve to be braver and possess higher speed and acceleration.
- If Safety or Cooperation
weight is higher, Guardlets will evolve to be more cautious and they will
keep together
- Modify the Max Energy Dose or
Max Safety Dose properties. This is another way to control evolution direction.
- Create a single new generation
by clicking the Breed button. Each selection of 'Breed' will produce a new
generation out of the current one.
- You can start the evolution process
with various types of populations:
- Start with a diverse, random
population.
Click 'Start Evolution'.
- Start with a homogeneous population.
Use the default population, or one you defined by changing environmental
parameters using 'Update' in the 'Edit Properties' screen.
- Select a predefined evolutionary
process from the Predefined screen.
- Limit the possible variation by
clicking Limit Ranges button.
This will ensure a more homogenous, less wild population.
- Examine the history of the evolution
by looking in the History page in the Info screen.
- Stop the evolutionary process
by clicking the Stop Evolution button.
(This toggle button displays the label 'Stop Evolution' when evolution is
on).
Discussion
The Emergent Behavior
The simple behavioral rules produce
interesting emergent behavior. When Guardlets are not disturbed by Attackers
they stick more or less together and meander in their home area. However, when
an Attacker is introduced it will begin to excite them. The emergent flocking
behavior they exhibit seems by its inherent mechanics to disrupt the process
of excessive Attacker resource consumption in this model.
The Evolutionary Process
The evolution mechanism is built
on three layers:
- The lowest layer is the genotype:
This is the actual chromosomal string on which the genes are encoded. The
Guardlets genetic algorithm is based on a string of hexadecimal characters,
where each group of 4 characters on the chromosome represents a specific trait.
At this level, we have only character strings that mean nothing until they
are interpreted.
-
Here is an example
of an encoded chromosome and each trait: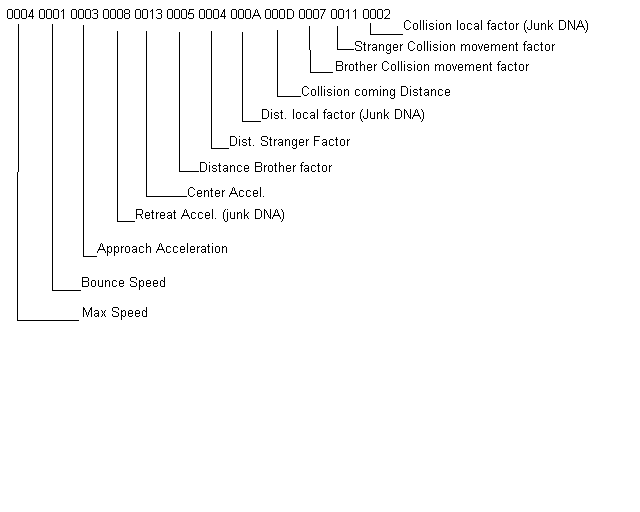
- The middle layer is the phenotype:
Here the information encoded in the genes is translated into behavior, which
can be seen in the real world; The Model. For example, a specific character
group in a specific location on the chromosome may define a specific Guardlet
acceleration. The Guardlet movement we see on the screen is influenced by
this value.
- The third layer is the evolutionary
fitness:
The fitness depends on the phenotypic properties, but not always in a direct
and simple way. There are no genes for fitness. A Guardlets's fitness is maximized
when both energy, safety, and cooperation are maximized.
So we have this chain:
Evolutionary selection is done by fitness, fitness depends on the phenotypic
traits, and these are defined by the genetic string. The evolutionary operators
themselves (reproduction, crossover and mutation), act on the chromosome string.
And the result can be unpredictable:
By modifying specific traits, we influence the emergent behavior in ways that
are not always easy to predict. When the evolution mechanism throws its blind
operators, there is almost nothing we can tell in advance. Therefore it is quite
interesting to watch the behavior and evolution of Guardlets, even in this very
simple system.
J. Groff
groffj@neocoretechs.com
